Download the comprehensive JAMB Syllabus for Home Economics 2025/2026 to kickstart your preparation for the UTME exam. This detailed PDF contains all the essential topics, content areas, and clear objectives that will guide your studies and ensure you are well-prepared for the exam.
By using this syllabus, you’ll gain a clear understanding of what to focus on, helping you stay organized and confident. You can aslo check the List of JAMB Recommended Textbooks for All Subjects – 2025/2026
JAMB Home Economics Syllabus
JAMB SYLLABUS FOR HOME ECONOMICS
GENERAL OBJECTIVES
The aim of the Unified Tertiary Matriculation Examination (UTME) syllabus in Home Economics is to prepare the candidates for the Board’s examination. It is designed to test the candidate’s achievement of the course objectives, which are to:
- Acquire knowledge on the concepts and principles of Home Economics education.
- Apply the principles of foods and nutrition to planning, selection, and preparation of meals and the adoption of food hygiene and safety.
- Equip students with knowledge and skills in clothing and textiles.
- Apply the principles of Home Management in housing and family living.
DETAILED SYLLABUS
| TOPICS/CONTENTS/NOTES | OBJECTIVES |
|---|---|
| SECTION A: HOME ECONOMICS EDUCATION | |
| 1. Home Economics | Candidates should be able to: |
| a. Meaning, scope and importance of Home Economics. | i. Examine the importance of Home Economics to the individual, family, and society. |
| b. Objectives and ideals of Home Economics. | ii. Identify the objectives of Home Economics. |
| iii. Determine the scope of Home Economics. | |
| 2. Areas/Careers in Home Economics | Candidates should be able to: |
| a. Home Management | i. Recommend possible vocations in the different areas of Home Economics. |
| – Interior decoration | ii. Relate skills required to each vocation. |
| – Credit management | iii. Assess the benefits of each vocation to the individual and society. |
| – Florist | iv. Identify current vocations in Home Economics. |
| b. Foods and Nutrition | v. Identify sources of career information. |
| – Catering | |
| – Dietetics | |
| – Nutritionist | |
| – Public Health Education | |
| c. Clothing and Textile | |
| – Fashion designing | |
| d. Family and Child development | |
| – Early and Childhood education | |
| e. Teaching | |
| f. Counseling | |
| g. Media | |
| h. Research |
Economics Syllabus
2. Methods and Tools of Economic Analysis
a. Scientific Approach:
i. Inductive and deductive methods
ii. Positive and normative reasoning
b. Basic Tools:
i. Tables, charts, and graphs
ii. Measures of central tendency: mean, median, and mode, and their applications
iii. Measures of dispersion: variance, standard deviation, range, and their applications
iv. Merits and demerits of the tools
Objectives:
Candidates should be able to:
(i) Distinguish between the various forms of reasoning
(ii) Apply these forms of reasoning to real-life situations
(iii) Use the tools to interpret economic data
(iv) Analyse economic data using the tools
(v) Assess the merits and demerits of the tools
3. The Theory of Demand
a.
i. Meaning and determinants of demand
ii. Demand schedules and curves
iii. The distinction between change in quantity demanded and change in demand
b. Types of Demand:
- Composite, derived, competitive, and joint demand
c. Types, Nature, and Determinants of Elasticity and Their Measurement:
- Price, income, and cross elasticity of demand
d. Importance of Elasticity of Demand to Consumers, Producers, and Government
Objectives:
Candidates should be able to:
(i) Identify the factors determining demand
(ii) Interpret demand curves from demand schedules
(iii) Differentiate between change in quantity demanded and change in demand
(iv) Compare the various types of demand and their interrelationships
(v) Relate the determinants to the nature of elasticity
(vi) Compute elasticities
(vii) Interpret elasticity coefficients in relation to real-life situations
4. The Theory of Consumer Behaviour
a. Basic Concepts:
i. Utility (cardinal, ordinal, total, average, and marginal utilities)
ii. Indifference curve and budget line
b. Diminishing Marginal Utility and the Law of Demand
c. Consumer Equilibrium Using the Indifference Curve and Marginal Analyses
d. Effects of Shift in the Budget Line and the Indifference Curve
e. Consumer Surplus and Its Applications
Objectives:
Candidates should be able to:
(i) Explain the various utility concepts
(ii) Apply the law of demand using the marginal utility analysis
(iii) Use indifference curve and marginal analyses to determine consumer equilibrium
(iv) Relate the income and substitution effects
(v) Apply consumer surplus to real-life situations
5. The Theory of Supply
a.
i. Meaning and determinants of supply
ii. Supply schedules and supply curves
iii. The distinction between change in quantity supplied and change in supply
b. Types of Supply:
- Joint/complementary, competitive, and composite
c. Elasticity of Supply:
- Determinants, measurements, nature, and applications
Objectives:
Candidates should be able to:
(i) Identify the factors determining supply
(ii) Interpret supply curves from supply schedules
(iii) Differentiate between change in quantity supplied and change in supply
(iv) Compare the various types of supply and their interrelationships
(v) Relate the determinants to the nature of elasticity
(vi) Compute elasticity coefficients
(vii) Interpret the coefficients in relation to real-life situations
RECOMMEDED POST:
- JAMB Syllabus for Physics 2025/2026: Free PDF Download
- JAMB Syllabus for Mathematics 2025/2026: PDF Download
- JAMB Syllabus for English Language 2025/2026: PDF Download
- Complete JAMB Syllabus for 2025: All Subjects with Recommended TextBooks
TOPICS/CONTENTS/NOTES & OBJECTIVES

 TOPICS/CONTENTS/NOTES & OBJECTIVES
TOPICS/CONTENTS/NOTES & OBJECTIVES  TOPICS/CONTENTS/NOTES & OBJECTIVES
TOPICS/CONTENTS/NOTES & OBJECTIVES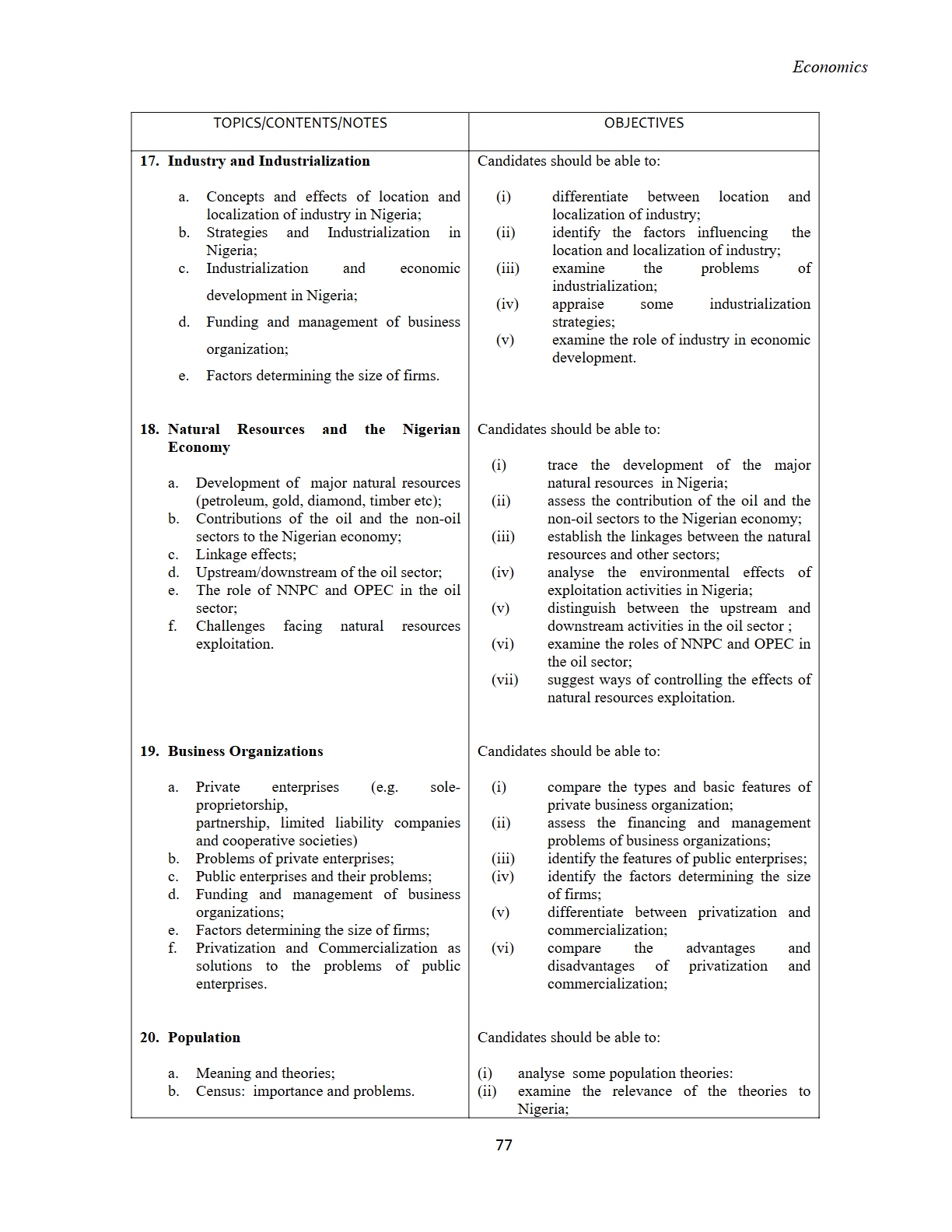 TOPICS/CONTENTS/NOTES & OBJECTIVES
TOPICS/CONTENTS/NOTES & OBJECTIVES
